What is snow?
Small and fragile crystals of icy water are snow. Thick and heavy snow cover can change the speed of rotation of the planet.
Snow is one of the varieties of precipitation. Small crystals form inside the clouds, falling to the surface in winter and in cold weather. Huge snow masses are made up of billions of small snowflakes.
How is snow formed?
Snow can be called frozen rain falling on the ground in winter, cold autumn and, periodically, in spring. Snow may form at temperatures below 0 degrees. Small drops of moisture in the rain clouds freeze, therefore this type of precipitation forms.
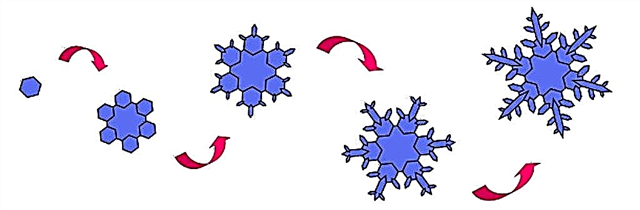
The smallest particles of water take the form of a hexagon, an ice crystal gradually turns into a hexagon. At a temperature of 15 degrees, the crystals become thin plates, and at 8 they turn into columns hollow inside. At a temperature of 2.5 degrees, they take the shape familiar to people in the form of snowflakes.
Snow may form due to evaporation of moisture. A similar phenomenon is clearly observed during drying of clothes in the cold. The fabric gradually becomes hard, freezing due to the presence of moisture in it. After this, the evaporation process begins, ice begins to break away from matter, evaporating up into the atmosphere. Evaporation of ice can last several days, after which the fabric becomes dry and soft again.
Snowflake texture

Snowflakes are made up of tiny particles of water. The structure at the molecular level is arranged in such a way that the corners of newly formed snowflakes of strict sizes are 120 and 60 degrees. At the ends and edges of snowflakes, small growths of crystals form, after which the layers continue to freeze. Thanks to these processes, snowflakes acquire such unusual shapes. However, most of the formations are star-shaped.
The main forms of snowflakes
Researchers have identified the main forms of snowflakes: in the form of needles, stars, dendrites, fluffy, columns, plates.
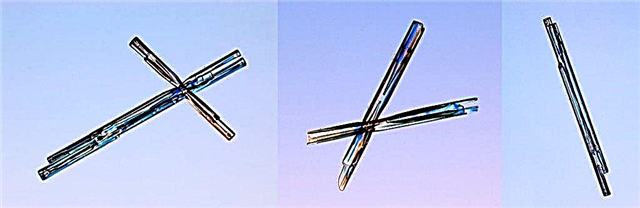
In the form of a needle - crystals resemble a special formation in the form of an ice spoke. They can be hollow inside with branched outgrowths on several sides.

Star shaped - crystals look like weave of ice fibers. They can be arranged arbitrarily, bending in different directions.
Interesting fact: snowflakes can be of various shapes and sizes. In total, 35 stable forms of formations are noted. They vary with the temperature and location of the clouds.

Dendrites - intergrown crystals of snowflakes, forming a symmetrical and branched outgrowths, diverging in different directions.
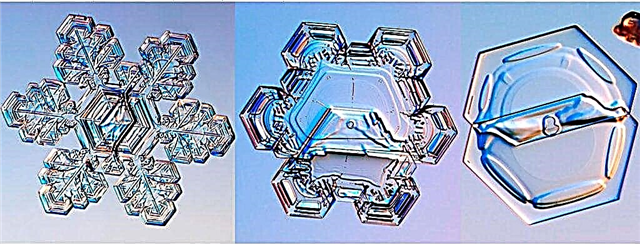
Fluffy snowflakes consist of several growths, which gradually broke or crushed. Basically, such snowflakes are obtained due to strong winds.

Columns - large flattened snowflakes. One of the most common forms of rainfall. Look like pillars, a sharpened hexagonal pencil.
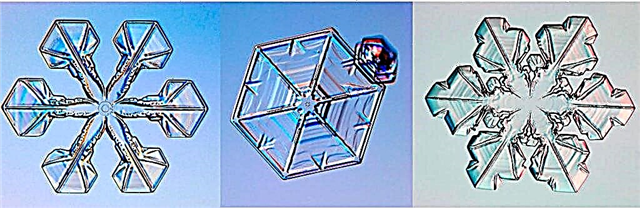
The plates are in the form of flower petals, divided into separate sections by ribs.
Interesting fact: Snow is considered a mineral. This theory was put forward by the National Data Center for the Study of Snow and Ice. Mineral, by definition, is a solid homogeneous substance, which has an inorganic origin, composition, particle arrangement. Snow is frozen particles of water. Water is turned into ice, which forms at a temperature below 0. Since ice is homogeneous and has its own unique structure, and also formed in an inorganic way, it fits the description of the mineral. And if ice can be considered a mineral, then snow too.
What determines the shape of snowflakes?
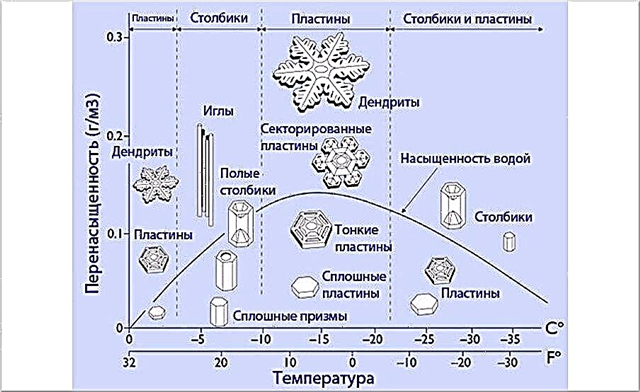
The shape of snowflakes can be different. At the moment, 48 species of formed snowflakes are distinguished. Shape may vary due to weather conditions.As a rule, the lower the temperature of the clouds, the higher they are located. Snowflakes appearing in clouds with temperatures from -13 to -16 take the form of stars. As you approach the earth's surface, snowflakes take the form of flat hexagons and needles.
Snow classification
Snow is a form of precipitation in the form of ice crystals, and not just frozen water. Due to the special location of water molecules, they take the form of a hexagonal prism. When falling, frozen crystals of water create phenomena such as:
- Frost
- Hail
- Snowfall
- Crystals of snow.
Snow flakes can be up to 30 cm one of the researchers of the phenomenon was Winson Bentley, who began to photograph crystals through a microscope. He took more than 5.5 thousand photographs. Then he discovered that every snowflake in nature is unique and not like the others.
Snow can also be divided according to criteria such as the mechanism of precipitation, color and intensity.
By the mechanism of precipitation, snow happens:
- Obligatory;
- Stormy;
- Snow drizzle.
Heavy snow

Heavy snow falls on vast territories from clouds of a uniform type. As a rule, this occurs during a ten-point cloud cover. Snowfall can last monotonously for a long time. Compound snow looks like a mass of dense small crystals. In such weather, poor visibility. In winter, just such snow predominates.

Heavy snow is the exact opposite. During this period of time, snow masses intensively fall to the ground. Snowfall begins and ends abruptly. It falls out of large cumulonimbus clouds when the atmosphere is extremely unstable.

Snow drizzle is characterized by a bunch of tiny snowflakes that create a haze in the air. It lasts from several hours to several days.
Snowfall

The time when snow falls from a cloud is called snowfall. Snowfalls are usually very intense, and can last up to several days. The intensity is distinguished by:
- Light snowfalls, whose flakes rarely occur - less than 10 per cubic meter of air around.
- Medium - from 10 to 100 snowflakes per cubic meter of air.
- Heavy snowfall with an intensity of 100 snowflakes per cubic meter of air.
Blizzard

It is the number of snowflakes that determines the main indicators of snowfall. In a period when a strong wind does not blow, snowfalls can be considered calm. During strong winds, snowfalls are called riding blizzards.
As a rule, snowfalls are predicted by meteorologists. Residents of the area in which the storm is supposed to begin are warned in advance of disasters. Snowfalls can go up to several days, they stop life even in the largest settlements. Due to drifts on the roads it is impossible to drive, power lines cease to function.
Avalanches
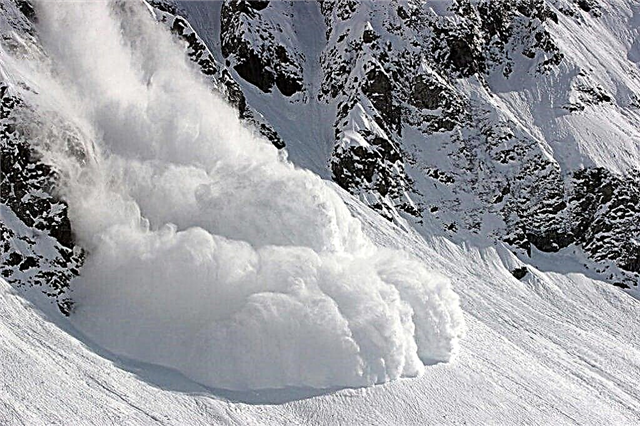

When enough snow accumulates, avalanches can occur. They descend from the slopes, destroying all the objects in their path. A person caught in an avalanche may not survive at all.
After snowfall, human and material sacrifices follow. Destroyed power lines, communication systems. Some cities may be blocked from civilization. In the world, cases have been recorded when entire centuries-old cities died under avalanches. Snowy avalanches move at a speed of 100 m / s. The volume of snow mass is up to two million cubic meters. When an avalanche begins to descend, it inevitably creates powerful shock waves from the air. One such wave can move a train or destroy a small building.
If a person is aware of the rules of behavior when caving in avalanches, he will be able to escape. To avoid problems, it is worth identifying for yourself the possible boundaries of the descent.
Interesting fact: Each snowflake, contrary to popular belief, is not unique. Under conditions with the same temperature and external factors, it is possible to obtain crystals that are absolutely identical in appearance and structure.In nature, such a structure can be found very rarely for a simple reason - all the snowflakes are deformed during the fall.
Snow melting

The most famous property of snow can be considered its melting at temperatures above zero. Snow usually melts in spring when the warm sun shines. However, not many people know that even at low temperatures in the sun, snow also begins to melt. Ice crystals evaporate from the surface, bypassing the process of turning into water.
When there is a lot of dirt on the street, snow melts several times faster - the dark color absorbs more heat. Therefore, it is not surprising that snow can lie in the forests until the beginning of summer. When ice is sprinkled with salt, its crystals begin to gradually break up. There is a transformation into a liquid state of aggregation. When the snow begins to melt, it becomes denser and heavier.
The benefits of snow
Snow is very useful: it covers the surface of the earth for the winter, keeps plants and small animals warm, helping them survive in difficult winter conditions. If there was no snow in winter, then yields will not grow - during melting, snow saturates the soil with much-needed moisture.
Snow turns into water and life begins again. Animals come out of hibernation, plants again make their way out of the ground. Life on Earth develops cyclically due to constant metamorphoses repeating annually.
Why does snow creak underfoot?

Since snow is a mass of crystals of various shapes, it begins to creak underfoot. Among millions of crystals there are also air molecules. When a person compresses part of the snow, then it begins to condense, crystals break, and air is forced out. That is why the sound of snow cod is created. In this case, the noise of breaking crystals can not always be heard.
Why does snow creak in cold weather, but not in warm weather?
When the weather is warm, some of the snow layer melts. Water begins to suppress all the noise of breaking crystals, so the sound is hard to hear. The most distinct sounds appear in severe frosts. The temperature changes periodically, so a small amount of water in the space between the snowflakes freezes.
If snow has fallen recently, then the density of contact of snowflakes to each other is extremely low. Old lying snow is much denser. Old snow makes a lower sound when compressed, more like a rustling sound.
Why is snow white?

The entire planet is surrounded by electromagnetic waves, invisible to the eye. They are absolutely everywhere and concentrate on the poles. Vision perceives these electromagnetic radiation as the color. Waves of electromagnetic radiation give us color sensations. The Sun is considered the main source of such waves.
The sun's rays contain a full range of shades. When all the colors merge together, it turns white. The sun's rays are just white. Snow and ice fully reflect sunlight. Each snowflake is a separate piece of ice, which also reflects the solar glow. Due to the fact that snowflakes lie on the surface in any order, form snowballs and blockages, they cannot completely pass electromagnetic radiation.

This can be checked in a simple way - just dig a small hole in the snow in sunny weather. Inside the hole, the snow will appear darker, slightly yellowish. In cloudy times, snow seems gray-blue at all. Thus, the appearance of snow directly depends on the weather around.
When the sun shines bright on the street, a snowdrift reflects the full spectrum of sunlight. This can be seen even with the naked eye - pure snow shimmers and seems to shine. Closer to the poles of the planet, snow takes on red hues. This is due to a special type of algae, which, when propagated, turns everything pink.
The famous Charles Darwin made notes about the different colors of snow in his diaries. Once he went on a long journey and noticed that his horse's hooves left red marks in the snow.Due to the bright sunset, the snow can also take other colors, as it reflects red light.
The concept of color is a subjective thing. Some people are unable to distinguish colors, some get confused in shades, and some come up with and distinguish their own unique shades.
Three different people can see the same object from a different point of view: for some, the grass will be emerald, for some it will be light green, while someone will generally see the turquoise blue in it. Color reproduction phenomena have not yet been thoroughly studied. It is only known that each person has his own perception of color, different from others.
Pink or watermelon snow
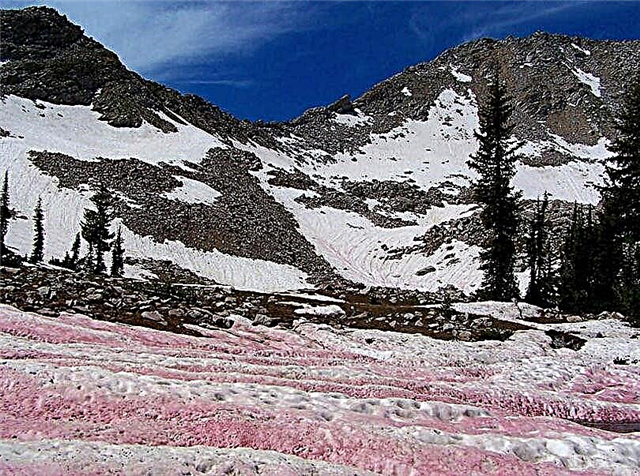

By color, snow is not only white. Pink snow does not come across very often. It can be found in Greenland, at the North Pole and on some mountains. Such snow occurs in the spring and summer. At this time, the sun slightly warms up the snow cover, the snow gradually gets wet. The wetter the snow becomes, the brighter its color. Red snow was spotted by Aristotle.
In the XIX century, such snow was brought to the UK. Then no one could explain the nature of the phenomenon. A nerd from Scotland, Robert Brown, suggested that the snow acquired this shade due to algae. He was right, and a century later, scientists revealed the activity of chlamydomonas in the snow. They began intensive reproduction even in the cold. When oxygen reached the algae, they began to smell like watermelons. According to some eyewitnesses, the snow also tastes like this fruit.
Thus, the white color of the snow was due to the fact that its surface fully reflects the spectrum. And when combining all the colors of the spectrum, it turns white. However, the color will also depend on the shades of the sky at the moment.
Snow on other planets
Part of the planets of the solar system is characterized by the presence of its own atmosphere. It may differ from the atmosphere of our planet, however, there are many similar features - in any atmosphere there are air flows. On Mars, there is both familiar snow and precipitation similar to snow in the form of carbon dioxide, best known as dry ice or dry snow.

Neptune's satellite also has snow from hydrogen and a mixture of various gases. At the same time, on Triton is not the usual white, but pink snow. It looks like this because of the complex compounds in its composition. Also, this snow forms under the strong influence of ultraviolet radiation. At each pole of this satellite, snow strata are located, up to several hundred meters in size.